Diamonds have long been a symbol of love, luxury, and status. However, in recent years, there has been a growing interest in the production of laboratory-grown diamonds as a more ethical and sustainable alternative to mined diamonds. In this article, we will explore the differences between a mined diamond and a laboratory-grown diamond.
Mined Diamonds:
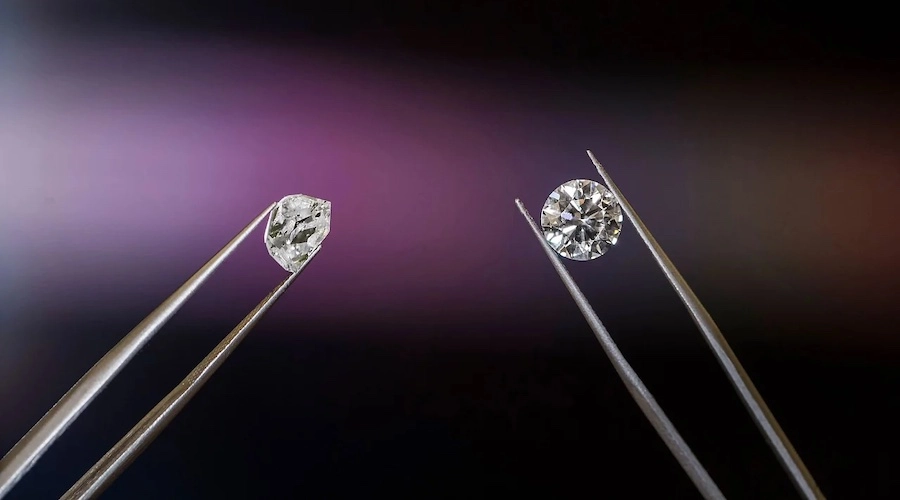
Mined diamonds are formed naturally over millions of years deep beneath the earth’s surface. These diamonds are found in mines, usually in remote locations, and are extracted using heavy machinery and explosives. The mining process is often associated with negative environmental and social impacts, such as habitat destruction, water pollution, and exploitation of workers.
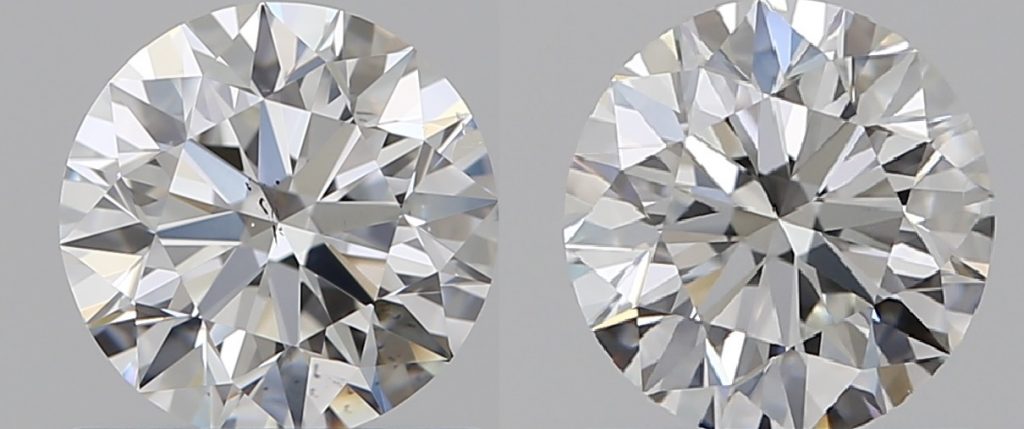
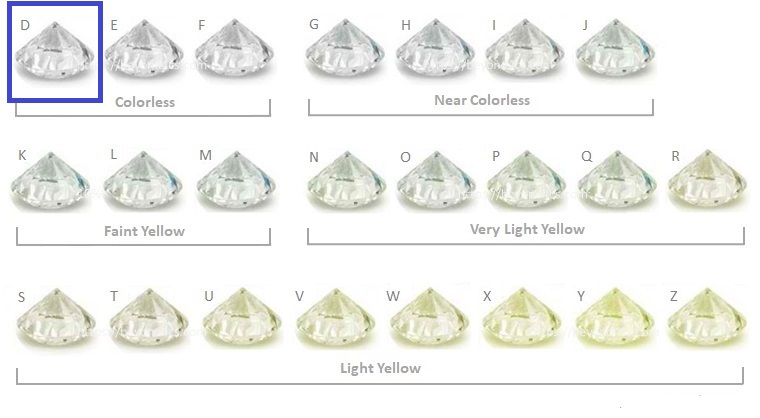
Mined diamonds are valued for their rarity and unique characteristics. The quality of a diamond is determined by the 4Cs – cut, clarity, carat weight, and colour. The more perfect a diamond is in each of these categories, the more valuable it is considered to be.
Laboratory-grown Diamonds:
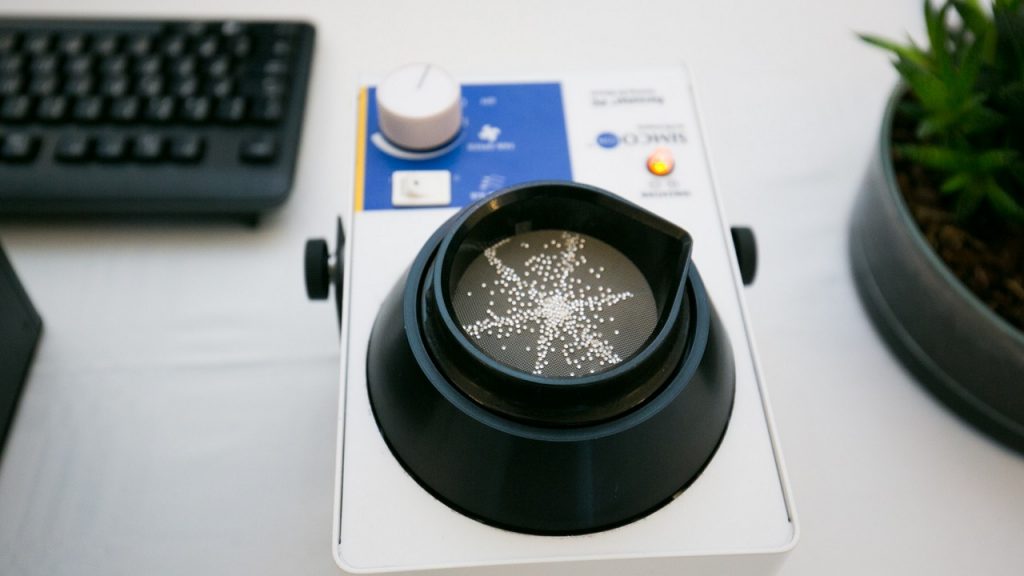
Laboratory-grown diamonds are created using advanced technological processes that mimic the natural formation of diamonds. These diamonds are produced in a laboratory environment, where conditions are controlled and monitored to ensure consistent quality and purity.
The process of creating a laboratory-grown diamond involves using a small diamond seed, which is placed in a chamber and exposed to extreme heat and pressure. Over a period of weeks, carbon atoms are deposited onto the seed, gradually building up the crystal structure of the diamond.
The resulting laboratory-grown diamond is physically and chemically identical to a mined diamond, and can be graded using the same 4Cs criteria.
Differences between Mined Diamonds and Laboratory-grown Diamonds:
Mined diamonds and laboratory-grown diamonds have very similar chemical properties, as they are both made of pure carbon atoms arranged in a crystalline structure. However, there are some subtle differences in the impurities and defects that can be present in each type of diamond.
Mined diamonds can contain trace elements such as nitrogen, boron, and hydrogen, which can affect the diamond’s colour and other properties. Laboratory-grown diamonds can also contain these impurities, but they can be controlled more precisely during the growth process to produce diamonds with specific colours and properties.
One key difference between mined and laboratory-grown diamonds is the presence of defects in the crystal structure. Mined diamonds can contain defects such as vacancies, dislocations, and impurity atoms, which can affect the diamond’s hardness and other physical properties. Laboratory-grown diamonds are typically more pure and have fewer defects, which can make them more consistent in their properties and easier to work with for industrial and scientific applications.
In terms of their chemical composition, both mined and laboratory-grown diamonds are made of pure carbon, with each carbon atom bonded to four neighboring carbon atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. This gives diamonds their unique hardness and other physical properties, as well as their optical properties such as high refractive index and dispersion.
Overall, while there are some subtle differences in the impurities and defects that can be present in mined and laboratory-grown diamonds, they are both essentially the same material in terms of their chemical properties.
One of the key differences between mined diamonds and laboratory-grown diamonds is their origin. Mined diamonds are natural, formed over millions of years in the earth’s mantle. Laboratory-grown diamonds, on the other hand, are created using advanced technological processes in a laboratory.
Another difference is the environmental and social impact of the two types of diamonds. Mined diamonds are often associated with negative environmental and social impacts, such as habitat destruction, water pollution, and exploitation of workers. Laboratory-grown diamonds, on the other hand, are generally considered to be more sustainable and ethical, as they do not involve the same level of environmental destruction or human exploitation.
Finally, there is a difference in price between mined diamonds and laboratory-grown diamonds. Mined diamonds are generally more expensive, due to their rarity and the high costs associated with mining and extraction. Laboratory-grown diamonds, on the other hand, are often less expensive, as they can be produced in larger quantities and do not require the same level of mining and extraction.
Conclusion:
Mined diamonds and laboratory-grown diamonds both have their pros and cons. While mined diamonds are valued for their rarity and unique characteristics, they are often associated with negative environmental and social impacts. Laboratory-grown diamonds, on the other hand, are more sustainable and ethical, but may be less valuable due to their artificial origin. Ultimately, the choice between a mined diamond and a laboratory-grown diamond comes down to personal values and priorities.
Source: Certin Diamond Insurance company