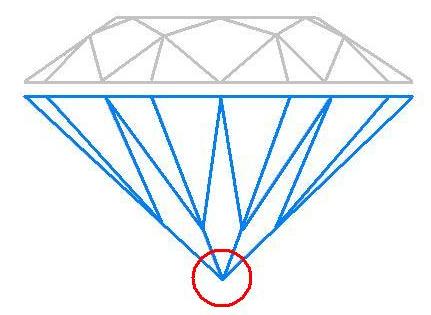
When looking closely at a diamond’s cut, one feature that often goes unnoticed is the culet. Though small, this detail plays a role in both the durability and the overall appearance of a stone.
Defining the Culet
The culet is the tiny facet at the very bottom of a diamond’s pavilion. Traditionally, it was cut to protect the fragile tip of the diamond from chipping or damage. In modern cutting, many diamonds are fashioned with either a very small culet or none at all, creating what appears to be a sharp point.
When viewed under magnification, a culet may look like a small circle in the centre of the diamond’s table (the flat top surface). Grading reports will often describe it using terms such as “None,” “Very Small,” “Small,” or “Medium.”
The Purpose of the Culet
Durability: The culet prevents the diamond’s pointed tip from breaking during setting or daily wear.
Light Performance: A well-proportioned culet has little to no effect on brilliance, but if the culet is too large, it can be visible through the table, appearing as a dark spot.
Aesthetic Tradition: Older cuts, such as Old European or Old Mine cuts, often feature larger culets, which are considered a hallmark of antique diamonds.
What if the Diamond Has No Point at the Bottom?

In modern cutting, some diamonds are designed without a defined point or traditional culet at the base. Instead of tapering to a sharp tip, the pavilion may finish with a flattened surface or an elongated structure.
This is sometimes informally described as a linear culet—a feature where the bottom of the stone forms a line or edge rather than a point.
Linear Culet – Not Standard Terminology
It’s important to note that “linear culet” is not a recognised term in official diamond grading systems. Laboratories such as GIA (Gemological Institute of America) or DCLA (Diamond Certification Laboratory of Australia) will not use this terminology on grading reports. Instead, they simply describe the culet as “None,” “Pointed,” or with size descriptors.
However, for a novice jeweller and clients, the term linear culet can be a helpful way of communicating what the eye perceives — especially in cases where the diamond clearly does not come to a point. Using this descriptive language provides clarity in conversation, even if it doesn’t appear on formal certificates.
Conclusion
The culet may be one of the smallest aspects of a diamond, but it reflects both the stone’s cutting tradition and the cutter’s intention to balance brilliance with durability. Whether pointed, open, or even described informally as linear, the culet is a fascinating detail that connects modern diamonds with centuries of cutting history.

Comments are closed