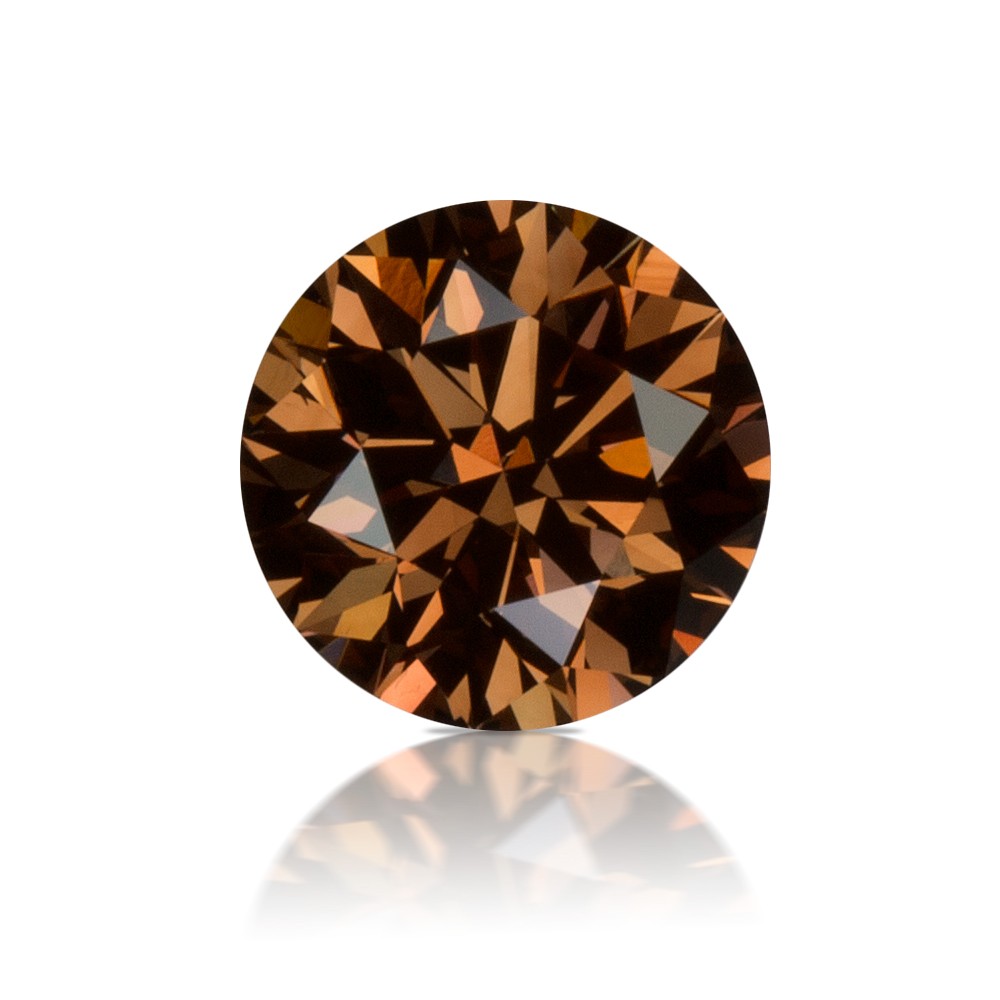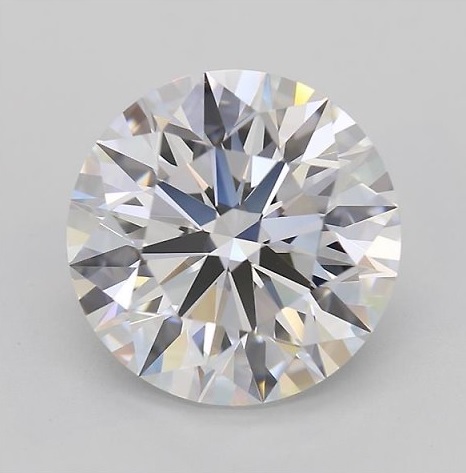
Colour
Diamond Colour is one of the most important factors in determining a diamond’s quality and value. DCLA[…]
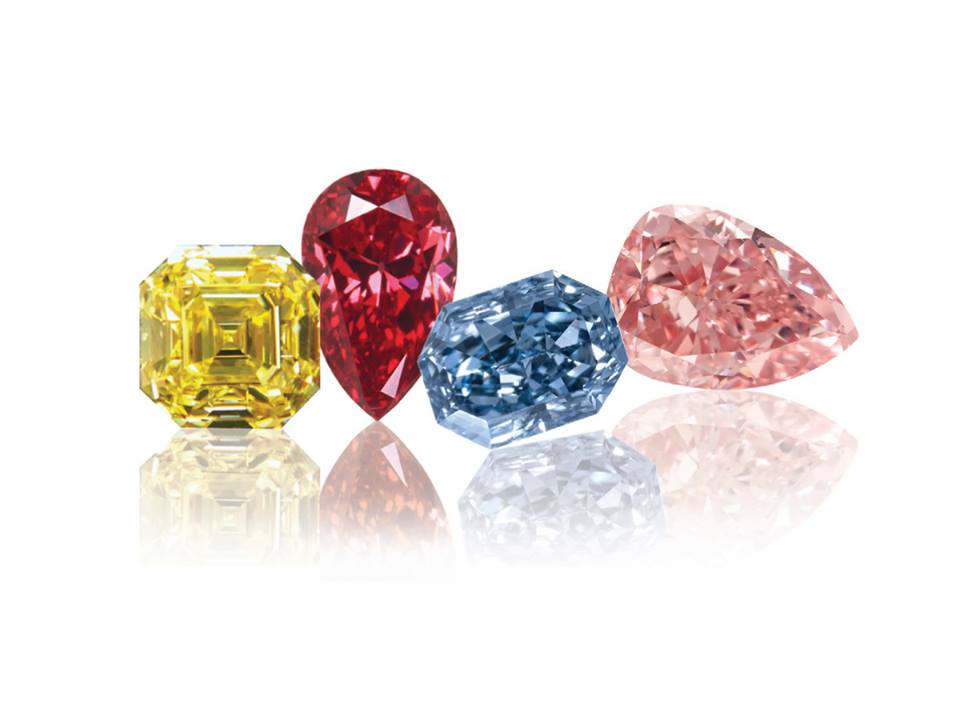

Coloured Diamond
A coloured diamond is a diamond that exhibits a hue other than the traditional colourless range.
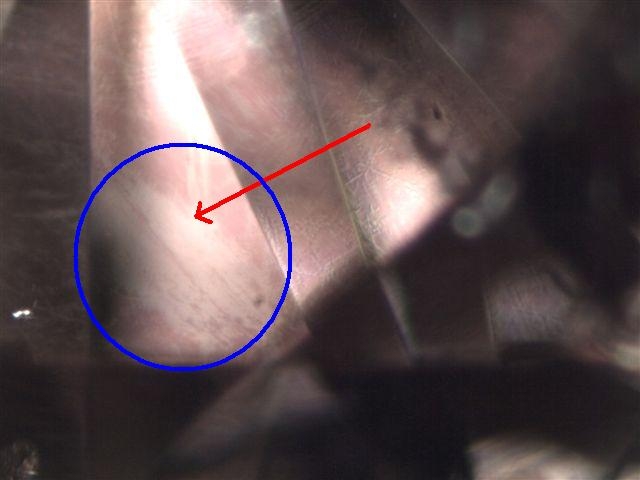
Coated Diamond or Coating
A coated diamond refers to a diamond that has undergone a treatment where a thin layer of[…]

Cold Laser Inscription
A diamond cold laser inscription is a process where a laser is used to etch a unique[…]
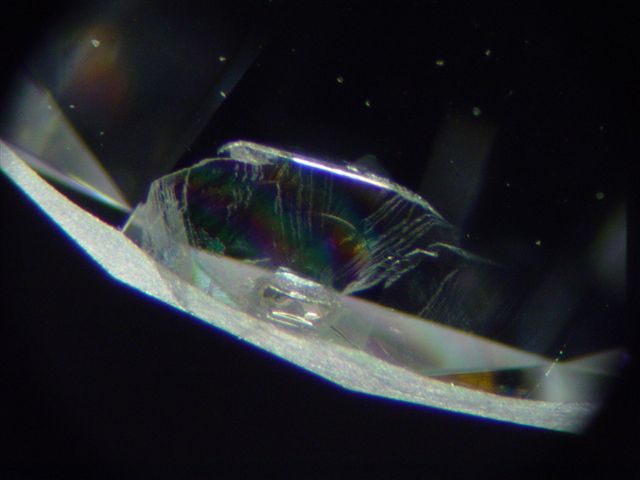
Cleavage
Cleavage in a diamond refers to the ability of a diamond to split or fracture along specific[…]

CIBJO
CIBJO, also known as The World Jewellery Confederation, is a global organization that represents the jewellery industry.[…]
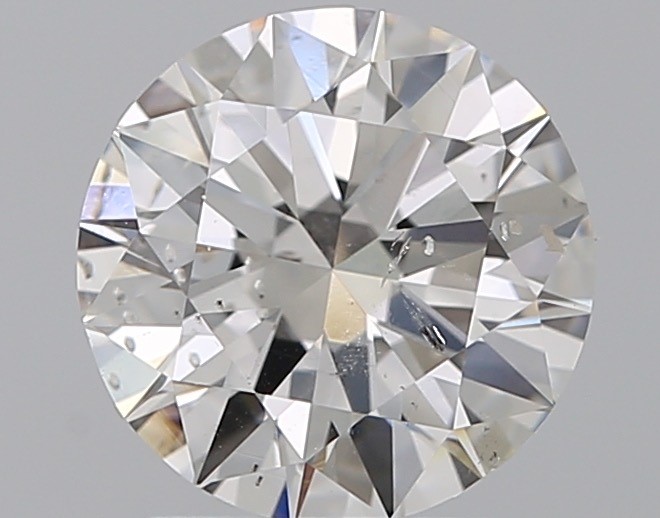

Clarity
Diamond clarity refers to the presence and visibility of inclusions (internal flaws) and blemishes (external flaws) within[…]



