- Depth

Diamond depth refers to the measurement of a diamond’s height, from the culet (bottom tip) to the table (top flat facet), as a percentage of its diameter. This is an important aspect of a diamond’s proportions and affects its overall appearance, including brilliance and sparkle.
The depth percentage is calculated as:
Depth Percentage=(Average Diameter Depth)×100
Ideal Depth Range:
The ideal depth percentage typically ranges from 59% to 62.5% for round brilliant diamonds. A diamond within this range is generally well-proportioned, optimizing light reflection and sparkle.
Impact on the Diamond:
Too Deep: If the diamond’s depth is too high (above 62.5%), it may appear smaller than its carat weight suggests because more of the diamond is concentrated in the pavilion (bottom). It can also lead to a loss of brilliance, as light may escape from the bottom of the diamond.Too Shallow: If the depth is too shallow (below 59%), the diamond can appear larger but may not reflect light as effectively. This can cause it to appear dull or lackluster, as light may escape through the sides.
The depth, along with other factors like the diamond’s table size, crown angle, and pavilion angle, plays a critical role in determining the diamond’s overall sparkle and visual appeal.
- Depth Percentage
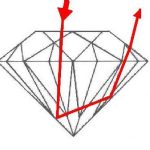
The diamond depth percentage is a key measurement used to evaluate the proportions of a diamond. It expresses the depth of the diamond as a percentage of its average diameter (width) and is essential in determining how well the diamond reflects light.
The formula for calculating the depth percentage is:
Depth Percentage=(Average Diameter of the DiamondDepth of the Diamond)×100
Depth Percentage Range:
Ideal Range: For a round brilliant cut diamond, the depth percentage typically falls between 59% and 62.5%. This range provides a good balance between size and brilliance, ensuring that the diamond reflects light well while maintaining an appropriate size.Shallow Depth: If the depth percentage is below 59%, the diamond may be considered shallow. This can cause light to leak out of the sides, resulting in reduced brilliance and a lackluster appearance.
Too Deep: A depth percentage greater than 62.5% can indicate that the diamond is too deep. This often leads to a smaller appearance for the carat weight, and may also reduce brilliance, as light escapes from the bottom of the diamond.
Ideal Proportions for Round Brilliant Diamonds:
Depth percentage: 59% to 62.5%
Table percentage: 53% to 58% (the percentage of the diamond’s top surface)
When considering diamond depth percentage, it’s important to also take other aspects of the diamond’s proportions into account, like the table percentage, crown angle, and pavilion angle, as they all work together to determine the diamond’s overall appearance and brilliance. - Diamond

A diamond is a precious gemstone composed of carbon atoms arranged in a crystal lattice structure, which gives it remarkable hardness and brilliance. It is the hardest naturally occurring material on Earth, making it highly prized not only for its beauty but also for its durability. Diamonds are formed deep within the Earth’s mantle under extreme heat and pressure over millions of years.
Key Features of Diamonds:
Hardness: Diamonds are rated 10 on the Mohs scale of hardness, meaning they are the hardest substance known to man. This makes them ideal for use in jewelry, especially rings and other items subject to daily wear.Brilliance: The unique structure of diamonds allows them to reflect and refract light in a way that creates their signature sparkle. The brilliance is largely determined by the diamond’s cut, which influences how light interacts with the stone.
Color: While diamonds come in a variety of colors, the most valued diamonds are those that are colorless or near-colorless. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) grades diamonds on a color scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). However, diamonds also come in fancy colors such as pink, blue, and yellow, which are graded on a different scale.
Clarity: This refers to the presence of internal or external imperfections, known as inclusions and blemishes, respectively. The fewer imperfections a diamond has, the higher its clarity grade. Clarity grades range from Flawless (FL) to Included (I1, I2, I3).
Carat Weight: The size of a diamond is measured in carats (ct), where 1 carat equals 0.2 grams. Larger diamonds are rarer and often more valuable due to their size.
Cut: The cut refers to how a diamond has been shaped and faceted, influencing how well it reflects light. The quality of the cut, rather than its shape (e.g., round, oval, princess), has the biggest impact on a diamond’s brilliance.
Types of Diamond Cuts:
Round Brilliant: The most popular and widely used cut, known for its maximum brilliance and sparkle.
Princess: A square or rectangular shape with pointed corners, offering a modern and sharp look.
Emerald: Known for its step-cut facets, which highlight clarity and offer a sophisticated, elegant style.
Cushion: A blend of round and square, with soft, rounded corners and large facets, giving a vintage feel.
Oval: An elongated shape, offering a unique, sophisticated appearance and a larger appearance compared to round diamonds of the same carat weight.
Natural vs. Lab-Grown Diamonds:
Natural Diamonds: Formed over millions of years under high pressure and temperature deep within the Earth.
Lab-Grown Diamonds: Created in a laboratory using high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) methods, which replicate the natural process. They are chemically identical to natural diamonds but can be more affordable.
Uses of Diamonds:
Jewelry: Diamonds are most commonly used in engagement rings, earrings, necklaces, and bracelets.
Industrial Applications: Due to their hardness, diamonds are used in cutting, grinding, and drilling tools.
Diamonds are not just symbols of luxury but also of endurance, making them ideal for celebrating significant milestones and relationships. - Diamond Bourse

A Diamond Bourse (also known as a Diamond Exchange) is a marketplace where diamonds are traded, bought, and sold by dealers, wholesalers, and manufacturers. These are typically private, members-only institutions that facilitate the trading of rough and polished diamonds. Bourses play a vital role in the global diamond industry by providing a structured environment for the exchange of diamonds, ensuring fairness, transparency, and liquidity in the market.
Key Features of a Diamond Bourse:
Membership: Only registered and qualified members, often diamond dealers or companies in the diamond trade, can participate in transactions. Membership requirements typically include a background check, an established business, and a proven track record in the industry.Trading: The bourse acts as a hub for diamond trading, with members displaying diamonds in booths or offices. The diamonds are typically sorted according to various factors, including size, cut, color, clarity, and certification.
Price Transparency: Diamond Bourses help establish and maintain current market prices for diamonds by facilitating trade and offering a place for price discovery. The presence of multiple buyers and sellers in a central location allows for competitive bidding and market price setting.
Security and Trust: Bourses are typically located in secure buildings, and transactions are closely monitored to prevent fraud and ensure that all diamonds traded meet agreed-upon standards. Many bourses also require that diamonds be certified by recognized grading institutions to ensure quality.
Global Influence: Some of the largest and most well-known diamond bourses have a global influence on diamond pricing and supply, such as the Antwerp Diamond Bourse (Belgium), the Israel Diamond Exchange (Israel), and the Dubai Diamond Exchange (UAE).
Auction and Direct Sales: Within a bourse, transactions may be made either through direct sales or auctions. In some cases, diamonds are auctioned to the highest bidder, while in others, the price is negotiated between the buyer and seller.
Prominent Diamond Bourses:
Antwerp Diamond Bourse (ADB): Located in Belgium, it is one of the oldest and largest diamond bourses in the world, known for facilitating a large volume of diamond trade.
Israel Diamond Exchange (IDE): Based in Ramat Gan, Israel, it is a key center for the global diamond trade, with thousands of traders and a strong focus on polished diamonds.
Dubai Diamond Exchange (DDE): A relatively new but influential bourse located in the UAE, contributing to the growing role of the Middle East in the diamond trade.
In addition to these, other cities with major diamond bourses include New York, Hong Kong, and Mumbai. These bourses ensure the smooth flow of diamonds through the global supply chain and contribute to the establishment of diamond market prices. - Diamond Dealers Club of South Africa

The Diamond Dealers Club of South Africa (DDC South Africa) is a prominent organization for diamond professionals in South Africa, serving as a hub for the trade, sale, and distribution of diamonds. The club’s primary aim is to promote and protect the interests of diamond dealers and traders, while providing a platform for them to conduct business in a secure and regulated environment.
Key Features of the Diamond Dealers Club of South Africa:
Membership: The DDC South Africa is a members-only organization, and only qualified individuals or companies involved in the diamond trade, such as diamond dealers, manufacturers, and wholesalers, can join. Membership requirements typically include a proven track record in the diamond industry and adherence to ethical standards.Trade Facilitation: The DDC provides its members with a structured environment to trade rough and polished diamonds, with members able to buy, sell, and exchange diamonds directly with one another. This helps streamline the trading process and ensures that transactions are conducted efficiently.
Security and Trust: Like other diamond bourses, the Diamond Dealers Club of South Africa ensures a secure trading environment, with stringent rules in place to prevent fraud, theft, and unethical practices. Members are expected to adhere to high ethical standards, contributing to a trustworthy marketplace for diamonds.
Networking and Collaboration: The club also serves as a platform for networking, allowing members to establish relationships, collaborate on business ventures, and share industry knowledge and insights. It is an essential resource for anyone looking to expand their reach within the South African diamond industry.
Market Influence: While smaller in scale compared to some of the major global diamond bourses (such as Antwerp or Israel), the Diamond Dealers Club of South Africa plays an important role in the regional diamond trade. South Africa is one of the world’s leading producers of diamonds, and the DDC helps maintain the country’s position in the global market.
Education and Training: The DDC may offer educational resources, workshops, and seminars to help members stay up-to-date on the latest trends, technologies, and market dynamics in the diamond industry.
Regulatory Support: The club often works closely with government bodies, industry regulators, and international diamond organizations to promote fair trade practices, ethical sourcing, and responsible diamond trading.
Location and Influence:
The DDC South Africa is based in Johannesburg, which is one of the world’s key diamond trading centers. Johannesburg’s position in the diamond supply chain makes the club an important part of South Africa’s broader diamond industry.
As a member of the World Federation of Diamond Bourses (WFDB), the Diamond Dealers Club of South Africa is part of a global network of diamond exchanges, contributing to the worldwide trade and exchange of diamonds.By providing a secure and efficient trading environment, the DDC South Africa helps foster a well-regulated and transparent diamond market, which benefits both the local industry and international trade.
- Diamond Dust

Diamond powder is a finely ground form of diamond that is used in a variety of industrial, scientific, and technological applications due to its hardness and unique properties. While diamonds are most commonly known as gemstones, diamond powder has many uses, primarily in fields that require precision cutting, polishing, and abrasives.
Key Uses of Diamond Powder:
Abrasives and Cutting Tools:Diamond powder is widely used as an abrasive material in industries where precision cutting, grinding, and polishing are required. Its extreme hardness allows it to effectively cut or grind through tough materials such as metals, ceramics, glass, and even other diamonds.
It is often used in the manufacturing of grinding wheels, polishing pads, and cutting tools, where it helps smooth, refine, and shape surfaces.
Polishing and Finishing:Diamond powder is used for polishing gemstones, including diamonds themselves, to achieve a high level of shine and smoothness. It’s also used for polishing other materials, such as metals and optical lenses, due to its fine abrasive properties.
In the jewelry industry, diamond powder can be used to polish and refine the facets of diamonds and other gemstones, improving their clarity and brilliance.
Laser and Micron Tools:Diamond powder is used in the production of laser-cutting tools and high-precision micro-tools, where its hardness and fine texture provide exceptional cutting efficiency and durability.
Electronic and Optic Manufacturing:In the electronics and optics industries, diamond powder is used for polishing lenses and mirrors that require high optical clarity. It’s also used in the manufacturing of semiconductors, where precision is critical.
Nanotechnology and Scientific Research:Diamond powder has applications in nanotechnology, where its fine particles can be used in research related to nanomaterials, coatings, and surface treatments. It’s also used in scientific equipment and tools that require a high degree of precision.
Diamond Powder Grades:
Diamond powder comes in various grades, depending on factors such as particle size and the specific application. Finer powders are typically used for polishing and delicate finishing work, while coarser powders are used for cutting and grinding.Synthetic Diamond Powder:
While natural diamond powder can be sourced from industrial diamonds, synthetic diamond powder is also widely available. Synthetic diamonds are produced through high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) methods or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes. These synthetic powders often have a similar hardness and physical properties as natural diamonds, but they can be produced more cost-effectively and in larger quantities.Diamond powder is indispensable in industries where extreme precision, cutting, and polishing are needed, making it a versatile and highly valuable material in modern manufacturing.
- Diamond Gauge

A diamond gauge is a precise measuring instrument used to assess the dimensions and other critical features of diamonds, such as diameter, depth, and sometimes even the quality of the cut. This tool is especially important in the jewelry and diamond industry to ensure that diamonds meet required specifications and standards.
Types of Diamond Gauges:
Diamond Thickness Gauge:This type of gauge measures the depth or height of a diamond, from the culet (the tip of the diamond’s pavilion) to the table (the top facet). Thickness gauges are essential for determining the overall proportions and ensuring that the diamond is properly cut for optimal light reflection and sparkle.
Diamond Diameter Gauge:A diameter gauge is used to measure the diameter of the diamond, particularly for round diamonds. The diameter is an important measurement in determining the overall size and weight of the diamond, and it helps determine the proper setting for the diamond in a piece of jewelry.
Micrometer or Digital Calipers:In some cases, a micrometer or digital calipers may be used as a diamond gauge. These instruments allow for highly accurate measurements, typically to the nearest hundredth of a millimeter. Micrometers are often used to measure small features, such as the diamond’s girdle thickness or the precision of the cut.
Gauge for Girdle and Table Size:A specialized gauge can be used to measure the width and thickness of the diamond’s girdle (the outer edge), and the size of the diamond’s table (the flat top surface). These measurements are important because they influence the diamond’s proportions and its ability to reflect light properly.
Facet Gauges:Some gauges are designed to measure the angles and dimensions of the facets on a diamond. These are important for determining the quality of the cut and ensuring that the diamond will achieve the desired brilliance and fire. They help assess the symmetry of the facets and the overall proportions of the diamond.
Importance of Diamond Gauges:
Accuracy: Diamond gauges ensure that diamonds are accurately measured and comply with the specific requirements set for various cuts and sizes.
Quality Control: By using diamond gauges, jewelers and diamond dealers can ensure that diamonds meet industry standards for proportion and quality, which affects both the aesthetics and the value of the diamond.
Certification and Grading: Diamond gauges are used in diamond grading and certification processes, such as those conducted by gemological laboratories like GIA or DCLA, to provide precise measurements that contribute to the overall grade and value of the diamond.
Overall, diamond gauges are essential tools in the diamond industry for precise measurement, quality control, and ensuring that diamonds meet the necessary standards for both beauty and value. - Directional Hardness

The bonds between carbon atoms that make up a diamond are stronger in some planes than others; this means that diamonds are marginally harder at some angles than at others. Diamonds thus have certain planes of weakness along which they can fracture, split or break. Directional hardness is related to the toughness and durability of diamonds.
Diamond directional hardness refers to the varying hardness levels that diamonds exhibit along different crystallographic directions. While diamonds are known for being the hardest natural material, their hardness is not uniform in all directions due to their crystal structure.
Diamond’s Crystal Structure:
Diamonds have a cubic (isometric) crystal structure, where each carbon atom is tetrahedrally bonded to four other carbon atoms, forming a very strong three-dimensional network. However, the strength of these bonds varies depending on the direction in which they are tested.Directional Hardness in Diamonds:
Hardness Along the Strongest Directions: Diamonds are hardest along the [111] axis, which is the direction along the diagonal of the crystal. This is where the carbon-carbon bonds are the most tightly packed, and the diamond’s crystal lattice is the most resistant to deformation. Along this direction, diamonds are extremely hard and maintain their hardness.Hardness Along the Weaker Directions: The [100] axis and the [110] axis are considered to be weaker directions in terms of hardness. While diamonds are still very hard along these axes, they are not as resistant to wear and scratching as along the [111] axis. In these directions, the atomic bonding is not as tightly packed as in the strongest directions.
Practical Implications of Directional Hardness:
Cutting and Polishing: When diamonds are cut, the direction of the cut is chosen carefully to exploit the hardest directions of the crystal, ensuring the diamond retains its brilliance and shape. Cutting along weaker directions can make the diamond more prone to chipping or cracking.Impact on Durability: While diamonds are incredibly durable overall, their directional hardness means that they can be more susceptible to damage if struck along certain axes, especially the [100] or [110] axes. Jewelers and diamond cutters take this into consideration when designing and setting diamonds.
Chipping and Cleavage: Diamonds can cleave or chip more easily along the weaker crystallographic directions, which is why it’s essential to handle diamonds with care during cutting and setting to avoid any damage along these axes.
Summary:
Diamonds are hardest along the [111] axis, and their hardness decreases along other axes such as [100] and [110].
Directional hardness plays a key role in diamond cutting, polishing, and setting, as the crystal’s strength varies depending on the orientation.
Understanding directional hardness is important for maximizing the durability and brilliance of diamonds, especially when they are subject to wear or impact. - Dispersion
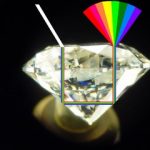
Diamond color dispersion refers to the way light is split into its component colors (a phenomenon called “fire”) as it passes through a diamond. This optical effect is one of the key features that contribute to the visual beauty of a diamond, as it results in the appearance of colorful flashes or “rainbows” when the diamond is moved or light hits it at different angles.
How Color Dispersion Works:
Diamonds have a high refractive index (the measure of how much light is bent or refracted as it passes through the material), which is one of the reasons they sparkle so much. When light enters the diamond, it bends and slows down due to its high refractive index. As the light continues through the diamond, it is then dispersed or split into its component colors, creating the rainbow-like effect.White light (from the sun or artificial sources) is composed of all colors in the spectrum, and the dispersion effect allows the diamond to separate these colors, showing them as flashes of red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. The more intense and vivid these flashes, the higher the dispersion.
The degree of dispersion is largely influenced by the diamond’s cut and the quality of its facets. Diamonds that are cut to maximize the path of light through the stone tend to display stronger color dispersion.
Factors Affecting Diamond Color Dispersion:
Refractive Index: Diamonds have a refractive index of 2.42, which is high compared to many other gemstones. This contributes to their excellent ability to refract and disperse light.Cut of the Diamond: The way a diamond is cut plays a significant role in its ability to disperse light. A well-cut diamond will have facets that are strategically placed to enhance the dispersion effect and maximize brilliance and fire. The angles and proportions of the cut are key factors in how light is channeled within the stone.
Diamond’s Dispersion Value: The dispersion of a diamond is measured by the difference in the refractive indices for red and violet light. Diamonds have a relatively high dispersion value, around 0.044, meaning they separate light into distinct colors. Some diamonds exhibit more noticeable “fire” or color dispersion than others, depending on their cut, size, and overall quality.
Fire and Brilliance in Diamonds:
Fire: The colorful flashes that appear due to dispersion are referred to as “fire.” A well-cut diamond with high dispersion can exhibit spectacular fire, especially when exposed to bright or varying light sources.
Brilliance: Brilliance refers to the white light that is reflected off a diamond’s facets. While dispersion creates colorful flashes, brilliance is the overall white sparkle you see from a well-cut diamond.
Comparison to Other Gemstones:
Diamonds have a higher dispersion than many other gemstones, like sapphires or emeralds, which is one of the reasons they are so visually striking.
Some gemstones, such as garnet or moissanite, have even higher dispersion values than diamonds, meaning they can display even more intense fire, but diamonds are still known for their exceptional balance of brilliance and fire.
Practical Implications for Diamond Buyers:
Fire and Visual Appeal: When selecting a diamond, many buyers are drawn to those that exhibit a strong fire effect due to higher dispersion. Diamonds that show flashes of vibrant color are often seen as more visually appealing.
Cut Quality: A diamond with a high degree of color dispersion is usually the result of an excellent cut. Poorly cut diamonds, even if they are of high quality, may not display the same fire due to improper light dispersion.
Summary:
Color dispersion is the splitting of light into its spectral colors, creating the characteristic “fire” in diamonds.
Diamond fire is a direct result of its dispersion ability, influenced by the diamond’s refractive index and cut.
Diamonds are renowned for their ability to exhibit color dispersion, contributing to their brilliance and visual allure. - Durability

Diamond durability refers to a diamond’s ability to withstand wear, scratching, chipping, and breaking over time. As the hardest naturally occurring substance on Earth, diamonds are renowned for their exceptional hardness, but their overall durability depends on several other factors as well. These factors include their toughness (resistance to breaking or fracturing), clarity (internal inclusions or flaws), and how they are handled or set in jewelry.
Key Factors Affecting Diamond Durability:
Hardness:Hardness is the measure of a material’s resistance to scratching. On the Mohs scale of hardness, diamonds score a 10, the highest possible rating, which means they can only be scratched by other diamonds.
This makes diamonds extremely resilient to surface damage from everyday wear, such as scratches from other materials like metals or other gemstones.
Toughness:Toughness refers to a material’s ability to resist fracturing or chipping when subjected to impacts. While diamonds are incredibly hard, they are not necessarily tough.
Diamonds have what is called cleavage, which means they have planes of weakness within their crystal structure. If struck with enough force along one of these planes, a diamond can chip, crack, or even break. This makes diamonds more susceptible to damage if not properly protected, especially from sharp impacts.
Clarity and Internal Inclusions:Diamonds that have significant inclusions (internal flaws) or cracks are more prone to damage. Inclusions can weaken a diamond and make it more susceptible to chipping or breaking under pressure.
High-quality diamonds with fewer inclusions tend to have better durability since there are fewer internal flaws that could potentially lead to cracks or fractures.
Cut:The cut of the diamond also plays a role in its durability. For instance, a diamond with sharp corners (like in a princess cut or emerald cut) is more likely to experience damage if exposed to forceful impacts compared to a diamond with rounded edges, such as in a round brilliant cut.
The way a diamond is set in jewelry can also affect its durability. For example, a diamond set in a prong setting might be more exposed to risks than one set in a bezel setting, where the diamond is surrounded by metal.
Size and Shape:Larger diamonds, particularly those with thin or pointed areas (like the corners of a princess cut), may be more vulnerable to chipping than smaller diamonds or those with rounder shapes. The girdle (the outer edge of the diamond) can also be a point of weakness if it’s too thin or if it’s exposed to rough handling.
Environmental Exposure:While diamonds are highly resistant to heat and most chemicals, they can be affected by extreme temperature fluctuations or harsh chemicals. For example, diamonds can fracture if subjected to rapid, extreme temperature changes (such as a sudden drop from a high heat environment to a cold one).
Chlorine bleach and other harsh chemicals can also affect a diamond, especially if the diamond has any inclusions or flaws.
Practical Considerations for Maintaining Diamond Durability:
Setting:
A secure and protective setting is crucial for diamond durability. For example, in a bezel setting, the diamond is surrounded by metal, which offers extra protection from impacts compared to a prong setting where the diamond is more exposed.
Cleaning and Care:
Regular cleaning with warm, soapy water and a soft brush will help maintain the diamond’s appearance and remove dirt, oils, or other materials that might accumulate over time.
Avoid exposing diamonds to harsh chemicals, including household cleaning products or chlorine, as these can cause damage to the diamond’s surface and any metal settings.
Avoid Hard Impacts:
Although diamonds are hard, they can still chip or break if struck with enough force along their cleavage planes. It’s advisable to remove diamond jewelry before engaging in activities where the diamond could be exposed to sudden impacts (e.g., heavy lifting or sports).
