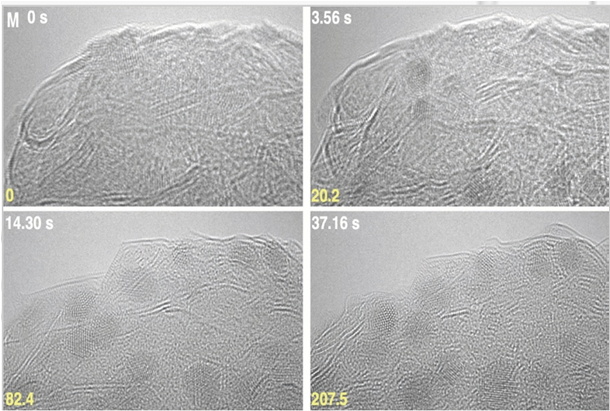
Researchers at the University of Tokyo say they’ve found a way to make tiny diamonds without the need for high temperature or high pressure conditions – unlike current lab grown technology.
They use electron beams to break and remake bonds in adamantane (C10H16), a carbon molecule in which atoms are arranged in a pattern very similar to the atomic structure of diamond.
The process takes tens of seconds under transmission electron microscopy conditions in a vacuum (low-pressure chamber)
A team led by Professor Eiichi Nakamura, of the Department of Chemistry, has published its findings in the journal Science, in an article entitled Rapid, low-temperature nanodiamond formation by electron-beam activation of adamantane C-H bonds.
It explains how the controlled electron irradiation of adamantane produces defect-free nanodiamonds.
The breakthrough process is aimed at creating tiny diamonds for high-tech industries, scientific research, and medical fields, rather than larger gem-quality stones.
It works through gradual assembly of diamond lattice from adamantane molecules under prolonged electron irradiation, which naturally limits the size to nanodiamonds currently.
Larger diamond growth would require controlling fusion of these nanocrystals and sustained lattice perfection over much longer times and at a larger scale.
Gem quality lab growns are created either using High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which uses high temperatures and low pressure.
Source: IDEX

Comments are closed